From Maronites to Muslims: Navigating Lebanon's Religious Heritage
Introduction
Brief History of Maronites in Lebanon
The Maronites, an Eastern Catholic group, have deep roots in Lebanon, tracing their origins back to the 4th century AD. The community is named after St. Maron, whose followers sought refuge in the rugged mountains of Lebanon. This geographical isolation allowed them to maintain their distinct religious practices and language over centuries.
Historically, the Maronites played a crucial role in the region. During the Crusades, they allied with Europeans, which strengthened their foothold and influence within Lebanon. The Maronite Patriarchate, established in the 16th century, became a focal point for the community, guiding both spiritual and political matters.
Key aspects of their history include:
- Survival and Resilience: Despite numerous challenges, including invasions and the Ottoman Empire's rule, the Maronites have preserved their identity.
- Political Influence: The Maronites were instrumental in shaping Lebanon’s modern identity, advocating for a balance between the various sects within the country.
Overview of Muslim Presence in Lebanon
Lebanon's religious landscape is not complete without the significant Muslim communities that have existed alongside the Maronites. Islam arrived in Lebanon in the 7th century, during a time of rapid expansion of the Islamic empire. This resulted in a rich tapestry of cultural and religious intertwining.
The Muslim population in Lebanon is primarily divided into:
- Sunni Muslims: Predominantly found in urban areas and coastal cities like Tripoli and Beirut.
- Shia Muslims: Concentrated in the southern regions and parts of the Beqaa Valley.
These diverse groups contributed to Lebanon's culture, politics, and economy, further enriching its multi-religious society. Their interactions with Maronite communities have shaped the country's complex history, showcasing a unique blend of coexistence and occasional tension.
As you can see, Lebanon's religious fabric is intricate, embodying centuries of history, struggles, and cooperation.
Maronites: Roots and Influence
Origins and Development of Maronite Christianity
The origins of Maronite Christianity are both fascinating and rich in history. Emerging in the 4th century, the Maronite Church formed around the teachings of St. Maron, a hermit whose devout life attracted followers in the mountains of Lebanon. This period marked the beginning of a resilient community that would endure numerous trials over the centuries.
- Isolation and Preservation: The mountainous terrain provided a natural barrier against invasions, allowing the Maronites to practice their faith freely and develop a unique cultural identity.
- Connection to the Catholic Church: In 1182, the Maronites formally recognised the Pope's authority, which solidified their relationship with the wider Catholic Church, fostering a sense of unity.
Over time, the Maronites not only withstood the pressures of surrounding empires but also contributed to the development of Lebanon's identity.
Maronite Cultural Contributions in Lebanon
The Maronite community's cultural impact on Lebanon is profound and multifaceted. From literature and music to art and architecture, the Maronites have left an indelible mark that still resonates today.
Some notable contributions include:
- Literature: Maronite scholars, such as the renowned Gabriel Sionite in the 17th century, published works that became cornerstones of Arabic literature and scholarship.
- Architecture: The series of impressive churches built throughout Lebanon reflect both Byzantine and Gothic influences. The Our Lady of Lebanon shrine in Harissa is a prime example, standing as a symbol of Maronite identity and faith.
- Music and Arts: Maronite religious hymns, particularly in the traditional 'Maronite Liturgy', enrich the country's cultural heritage, blending religious themes with local musical styles.
You can sense the vibrancy in Maronite celebrations, like Easter and Christmas, when communities come together, demonstrating commitment to their traditions. The Maronite Church not only provides spiritual solace but also acts as a cultural beacon, illuminating the diverse tapestry of Lebanon.
Islam in Lebanon: A Historical Perspective
Spread of Islam in Lebanon
The spread of Islam in Lebanon is a captivating chapter in the country's comprehensive history. It began in the 7th century when Arab armies expanded their reach following the death of the Prophet Muhammad. As they moved through the region, Lebanon became a melting pot of cultures and beliefs.
- Cultural Exchanges: Initially, Islamisation didn't erase the existing Christian communities; instead, it fostered a dialogue between different religions.
- Establishment of Islamic Sects: By the 13th century, Lebanon had witnessed the rise of various Islamic sects, including Sunni and Shia, each contributing to the diverse tapestry of Lebanese society.
The complex relationship between these groups enriched the cultural and social landscape of Lebanon, making it a unique hub of religious coexistence.
Impact of Muslim Dynasties on Lebanese Society
As various Muslim dynasties ruled over Lebanon, they left a lasting impact on the nation's development:
- Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates: These early empires introduced administrative systems that shaped local governance. They encouraged trade and cultural exchanges that thrived in cities like Tripoli, connecting Lebanon to a wider Islamic world.
- Mamluks: During their reign in the 13th century, they focused on architecture and infrastructure. The famous Mamluk mosques that dot the Lebanese landscape today, like the Great Mosque of Tripoli, showcase their contributions to urban development.
- Ottoman Empire: From the 16th to the early 20th century, the Ottomans further solidified Islam's presence in Lebanon through legal frameworks and social structures that promoted coexistence among the diverse communities.
These historical layers illustrate how Islam has woven itself into the fabric of Lebanese identity. It is not merely a religion but a significant part of the everyday life and culture in Lebanon, providing a rich heritage cherished by many.

Interactions and Coexistence
Maronite-Muslim Relations Through History
The history of Lebanon is characterized by a dynamic interplay between Maronites and Muslims, illustrating both challenges and cooperative efforts. From early on, these two communities found ways to coexist despite periods of tension and conflict.
- Historical Alliances: During the Crusades, the Maronites and Muslims faced external threats together, occasionally forming alliances to defend their homeland. This mutual interest in security initiated dialogues that transcended religious boundaries.
- Political Cooperation: Throughout various political frameworks, both communities have served in leadership roles. The establishment of the National Pact in 1943 was a significant milestone, as it aimed to ensure power-sharing and foster harmony between Christians and Muslims.
However, these relations were not without strife, with notable conflicts breaking out, particularly during the Lebanese Civil War. Yet, the desire for peaceful coexistence has often prevailed, leading to reconciliation efforts in more recent years.
Religious Diversity and Tolerance in Lebanon
One of the most remarkable features of Lebanese society is its deep-rooted religious diversity and the tolerance cultivated among its different faiths. This aspect of Lebanese culture is evident in everyday life.
- Cultural Celebrations: Nationwide holidays, including Ramadan for Muslims and Christmas for Maronites, are often celebrated together, showcasing a spirit of community and respect. It’s not uncommon for friends from different religious backgrounds to share meals and participate in each other’s festivities.
- Interfaith Initiatives: Numerous organisations strive to promote interfaith dialogue and understanding. Programs aimed at teaching respect for different beliefs in schools are increasingly popular, nurturing a new generation that values coexistence.
In a country where multiple religions share the same space, the emphasis on tolerance highlights Lebanon's resilience. It’s this unique blend of cultures, alongside a shared history, that enriches the Lebanese identity and paves the way for a hopeful future of peaceful coexistence.

Challenges and Dynamics in Contemporary Lebanon
Role of Religion in Lebanese Politics
In contemporary Lebanon, the role of religion in politics is profound and multifaceted. Lebanon's unique confessional political system mandates that leadership positions are allocated among various religious sects, including Maronites, Sunni Muslims, and Shia Muslims. While this arrangement was intended to promote equality and representation, it often led to political gridlock and sectarian tensions.
- Power Sharing: The National Pact of 1943 established a framework for sectarian power-sharing, which still influences politics today. While it aimed to cultivate stability, it has sometimes reinforced divisions rather than fostered unity.
- Political Influence of Religious Leaders: Religious figures often wield significant influence in political matters, impacting decision-making within their communities. This dynamic can perpetuate sectarian identities, sometimes at the expense of national cohesion.
In recent years, Lebanon has faced serious challenges, including governance failures, corruption, and economic turmoil, making the intertwining of religion and politics even more contentious.
Socioeconomic Factors Affecting Religious Communities
The socioeconomic landscape in Lebanon further complicates the dynamics between religious communities. Both economic challenges and regional crises have disproportionately affected certain groups, often leading to feelings of marginalisation and strife.
Some key factors include:
- Economic Disparities: The economic collapse has affected all communities, but some religious groups, particularly in rural areas, feel they bear a heavier burden due to the lack of resources and support.
- Emigration Trends: Many young professionals and skilled workers are leaving Lebanon in search of better opportunities abroad, which not only affects economic stability but also erodes the socio-cultural fabric of local communities.
- Refugee Presence: The influx of Syrian refugees has strained resources, leading to increased competition for jobs and services, which can heighten tensions among existing communities.
Navigating these multifaceted challenges requires a concerted effort towards understanding each community's unique context. While the road ahead remains fraught with difficulties, fostering dialogue and collaboration among Lebanon's diverse groups may pave the way for a more equitable and stable future.
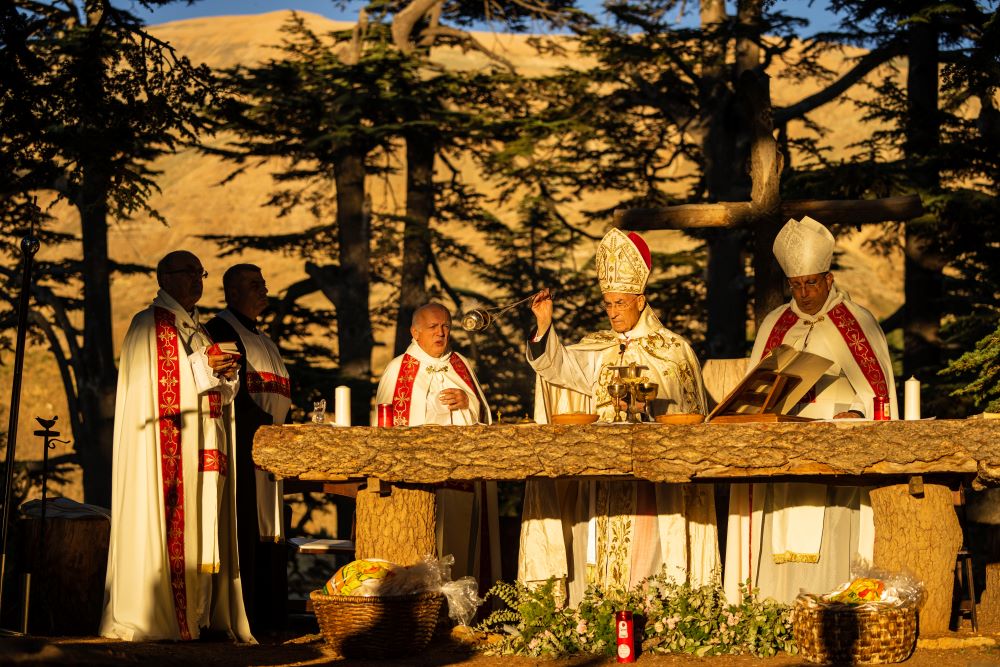

Preserving Lebanon's Religious Heritage
Efforts to Safeguard Religious Sites
Preserving Lebanon's religious heritage is not just about maintaining buildings; it's about safeguarding the stories, cultures, and traditions they embody. Lebanon is home to a rich tapestry of religious sites that reflect its diverse history, and concerted efforts have been made to restore and protect these treasures.
- Restoration Initiatives: Many religious sites, including the historic churches of Byblos and the ancient mosques in Tripoli, are undergoing restoration, funded by both governmental and international organisations. These projects aim to revitalize the areas while preserving their historical significance.
- Community Engagement: Local communities are often involved in these efforts, fostering a sense of ownership and pride. For instance, many neighbourhoods organize events that bring people together to clean and renovate older sites, reinforcing bonds among different religious groups.
Such initiatives exemplify how preserving physical spaces can promote a sense of shared identity, even amidst differences.
Promoting Interfaith Dialogue and Understanding
Interfaith dialogue is crucial for nurturing mutual respect and understanding among Lebanon's diverse communities. Various organisations and grassroots movements are dedicated to bridging gaps between faiths, working towards a peaceful coexistence.
- Educational Programs: Schools frequently incorporate interfaith education, teaching children about the beliefs and practices of different religions. This early exposure fosters empathy and reduces prejudices.
- Cultural Events: Festivals celebrating cultural diversity are organised, encouraging participation from various religious groups. Events like these often involve music, cuisine, and art, allowing different communities to appreciate one another’s heritage.
- The Role of Technology: In this digital age, social media campaigns and online forums have emerged as powerful platforms for promoting tolerance. Sharing stories of interfaith collaborations can inspire others and highlight positive examples of coexistence.
These efforts reflect a growing recognition of the importance of dialogue in a society built on diversity. While challenges remain, the commitment to preserving Lebanon's rich religious heritage through restoration and understanding lives on, offering hope for a harmonious future.
Conclusion
Reflections on Lebanon's Rich Religious Tapestry
As we step back and reflect on Lebanon's rich religious tapestry, it's clear that the country's diversity is both its strength and its challenge. From the vibrant traditions of the Maronites to the deep-rooted histories of the Muslim communities, every faith contributes to an intricate mosaic that defines Lebanon. This blend of cultures and beliefs fosters a lively social atmosphere, especially during festive occasions when people of different faiths come together.
- Cultural Synergy: Events like the Ashoura and Christmas celebrations often see cross-community participation, highlighting the shared values of love and unity.
- A Living Heritage: The historic sites scattered throughout Lebanon serve as physical reminders of the shared past, showing how generations have intertwined their histories.
Such interactions illustrate the potential for harmony in a complex environment, and they give us insight into the ways in which communities can work together despite their differences.
Importance of Preserving Religious Heritage for Future Generations
Looking to the future, preserving Lebanon's religious heritage is of paramount importance. By safeguarding these cultural treasures, we ensure that future generations can appreciate and learn from the lessons of the past.
- Cultural Identity: Maintaining religious sites and practices fortifies each community's identity, allowing individuals to embrace their heritage with pride.
- Educational Foundations: Programs focused on the history of religious coexistence can educate young people about the importance of unity in diversity, nurturing a more tolerant society.
In essence, the preservation of Lebanon's religious heritage goes beyond merely maintaining structures; it's about ensuring that the stories, lessons, and shared experiences of different faiths endure. By cherishing and promoting this diversity, we can hope to build a more understanding and unified Lebanon for generations to come, creating a legacy of peace and respect that resonates well into the future.
